Wearable sensor technology is an emerging technology in healthcare that enables continuous monitoring of patients’ vital signs and physical activity. Here are some ways wearable sensors can be used in healthcare:
1. Continuous monitoring of vital signs:
Wearable sensors, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, can continuously monitor patients’ heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation, giving healthcare providers real-time insight into patients’ health. Continuous monitoring can help in the following domains:

- Early detection of health issues: By continuously monitoring patients’ vital signs and physical activity, wearable sensors can help detect early signs of health problems, such as changes in heart rate or blood pressure, and alert healthcare providers to potential issues.
- Improved chronic disease management: Wearable sensors can help patients with chronic diseases, such as diabetes, better manage their condition by monitoring their blood glucose levels and alerting them to potential problems in real time.
- Increased physical activity: Wearable sensors can motivate patients to increase their physical activity by tracking and providing feedback on their progress.

- Remote patient monitoring: Wearable sensors allow healthcare providers to monitor their patients remotely, reducing the need for in-person visits and increasing the efficiency of care.
- Maternity monitoring: Wearable sensors can collect real time biometric data during the pregnancy to avoid complications in high risk patients. For example, wearable devices containing heart rate, blood pressure or ECG sensors can monitor the health of pregnant women and their fetuses.

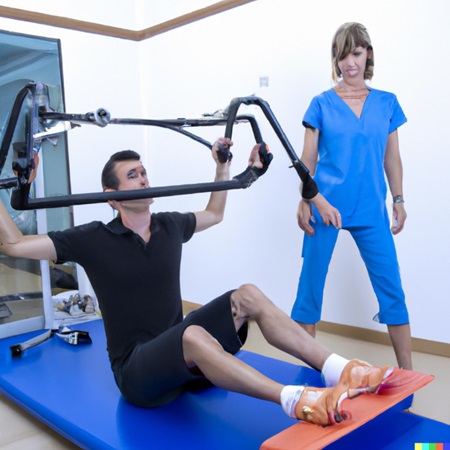
2. Rehabilitation and physical therapy:
Wearables such as wearable exosuits and smart clothing can help patients with their rehabilitation and physical therapy. These devices provide feedback and guidance to help patients perform exercises correctly, monitor progress, and adjust treatment plans as needed.
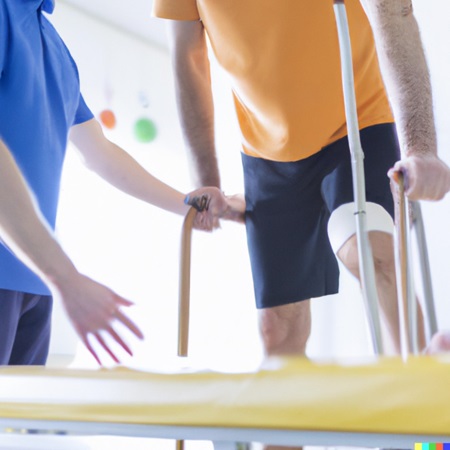


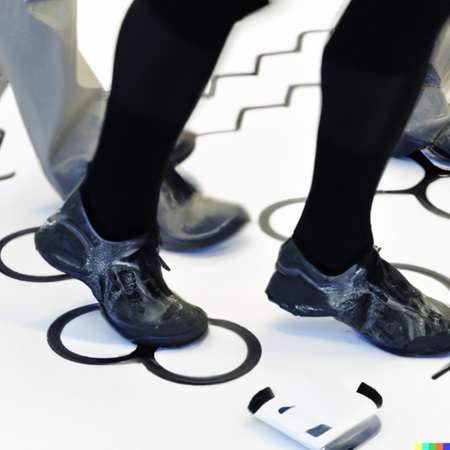
3. Gait Analysis for Fall Detection:
Human locomotion is accomplished through a complex interaction of muscles, skeleton and nervous system. Possible impairments of one of these anatomical systems can be detected early on by experts using a gait analysis. Such an analysis can be performed using wearable sensors in which small, lightweight sensors are attached to the body to collect data on a person’s walking patterns. The sensors can be placed on different parts of the body, such as the feet, legs, hips, or trunk, and can measure various aspects of gait, including stride length, step width, cadence, and foot pressure.
Wearable sensors used for gait analysis typically include accelerometers, gyroscopes, and pressure sensors. These sensors can be incorporated into a variety of devices, such as smart shoes, insoles, or fitness trackers. The data collected by these sensors can be analyzed using software algorithms to provide insights into a person’s gait patterns.


4. Pain Detection and Monitoring:
Analyzing pain perception is of great importance in numerous medical applications. For example, pain, or especially the pain threshold, in physiotherapeutic treatments can not only determine the course or the result of the treatment, but also shape the structure and composition of the exercises right from the start. The quantitative assessment of one’s own pain is traditionally based on self-assessment using questionnaires. However, this method is not an option for patients who are unable to (objectively) communicate their pain.


5. Flow Experience:
Individual and team flow is a concept with great potential for promoting team effectiveness, but measuring and promoting it is a challenge. Traditional measures of team flow rely on self-assessment questionnaires that require a disruption in the team process. Artificial intelligence approaches, i.e. machine learning, provide methods for identifying an algorithm based on behavioral and sensory data, capable of determining team flow and its dynamics over time.

It is important to note that while wearable sensors have great potential to improve healthcare, there are privacy and security concerns with using this technology. It is important to ensure that data collected by wearable sensors is properly secured and protected to prevent unauthorized access.